In Maryland the blue crab has been the dominant contributor to the seafood harvesting and processing industry. Employing over 1,200 workers, and in 1999 produced sales volume estimated at $30.3 million. Combined Maryland and Virginia dockside harvest for the year 2000 being $50.4 million, while the lowest catch in 20 years, weighed in at 50.9 million pounds. Crabmeat production occurs in approximately 44 processing plants along the Chesapeake Bay area. In Maryland, 60% of commercial watermen's fishing income came from the blue crab harvest. Over the last five years the market has had to compete with a large increase in imports of crabmeat
from Mexico and Indonesia.
The expansion of the market for softshell crab has been emphasized with a coinciding increase in crab shedding systems used to take advantage of the softshell market.
The world demand for the softshell, which is nearly
100% female crabs, has increased steadily and marketedly.

Female Crabs:
The Softshell Blue Crab Contradiction.
Softshell blue crabs, and the unknown global increase in demand for the product.
Softshell blue crabs have become a delicacy in many parts of the world as purveyors extended their markets. The softshell crab is prepared fresh, but most likely frozen and shipped. Only in your very best restaurants will you get "fresh-live" softshell blue crabs preparations.
Here is the big dilemma. Almost 100% softshell crabs are females.
NOBODY talks about this.
Packaged crabmeat, once solely male blue crabs, is now being replaced by packaged female crab meat as the male crab population has decreased in size and population.
If you want to invigorated the blue crab species in the Chesapeake Bay and Coastal Bays near Ocean City Maryland stop taking the female crab. The action needed - moratorium on softshell crab fishing and female crabs harvesting, and the crab population will come back.
How do they catch softshells ? They don't. They catch female hard crabs, and put them in pens until they molt. Dredging equipment shreds softshells, softshells don't crawl into traps because they bury themselves in the mud and submerged aquatic vegetation for protection while they are defenseless during the molting process. Submerged aquatic grass, hiding place for crabs during their molting process, has decreased from other fishing methods and pollution, further inhibiting the reproduction of the blue crab. Female
blue crabs are kept, and then harvested for softshells.
EXCEPT you will find in every Korean type grocery
store in the metropolitan areas the wholesale selling
of live female blue crabs as a substitute for the more
expensive male blue crab. Usually around $2.99
a pound or $10 a dozen or less.
Blue Crab's Reproductive Process has decreased the crab population.
Although female crabs only mate once, nearly 95 percent of all females are mated. Mating generally occurs in late summer.
1.) Female crabs mate once during their terminal molt, while males mate multiple times during their life. Mating can occur only while the female is in the soft shell state. Unlike males, females mate only once. Sperm may live in female seminal receptacles for a year or more and be used for repeated fertilizations.
Thus taking a female crab, which upon inspection is not showing evidence of egg sacks, should not be done. For the female still has the ability to reproduce.
2.) The ability for the males to effectively reproduce has declined because of their size and environmental stresses. Larger crabs are more effective impregnating the female. Since the harvest of crabs is dependent upon the size of the crab, and the demand for larger crabs versus small crabs is greater, the smaller crabs left in the population are less effective in reproducing. Environmental stress like pollution further decreases the male crabs potency. At any time, a males sperm for reproduction may only be at 50%.
These factors reduce the chances of a successful reproductive cycle of the crab.
FALL MIGRATION OF BLUE CRABS
 Males will stay in the upper portions of the bay and tributaries. Males will stay in the upper portions of the bay and tributaries.
 Newly mated mature females will migrate toward the mouth of the Bay. Newly mated mature females will migrate toward the mouth of the Bay.
 Immature females will be found mostly in lower to mid-Bay tributaries Immature females will be found mostly in lower to mid-Bay tributaries
 Mature females will primarily over-winter in the bay mainstream south of the Rappahannock River and prepare for spawning the following spring. Mature females will primarily over-winter in the bay mainstream south of the Rappahannock River and prepare for spawning the following spring.
 Females will not return to Maryland. Females will not return to Maryland.
 Females stay in Virginia waters until death. Females stay in Virginia waters until death. |
 |
In the fall... the male population of crabs reside in the upper bays, and the female population migrates towards the mouth of the bay in Virginia. This results in over harvesting of the females, the egg bearing of the species, and results in depleting the population as a whole. Females will carry male conception for continued reproduction even after first egg producing cycle. They do not need to re-mate.
The Overall Blue Crab Harvest Has Been Cut In Half
Fishing efforts targeted at females crabs has intensified.
In the early 1990's mature females comprised approximately 27% of the Maryland harvest. Now the harvest of the female exceeds 40%. The peeler crab, which is primarily immature females, was 8% and now exceeds 16% in Maryland.
This same pattern exists in Virginia's harvest of the blue crab.

The charts from 1999
and the above map shows us three things.
1.) The amount of FEMALE crabs harvested is greatly misunderstood, and increasing.
2.) Closing down the upper bays in Maryland does little to help fertilize the
female population not returning to the area.
3.)
The unrestricted harvesting of the female population at the mouth of the bay in Virginia depletes the reproduction of the egg bearing females and the species as a whole.
------------------------------
Mr. Ralph Giove, from Isle of Wight (on the west Bayside of Ocean City, Maryland) has also expressed his concerns about the dwindling crab population, specifically the over harvest of the female crab. In a phone conversation with Mr. Giove he expressed his concerns.
"The crab harvest in Maryland waters will not increase until some kind of restrictions are put in place to limit and protect the female crab. Especially
for the 'peeler' and 'softshell' blue crabs."
"Mr. Giove explains the female crab goes through three stages of her life. The virgin stage, the soft shell stage, the mature stage.
The virgin stage are the very young crab, also known as peeler crabs. These female crabs are very valuable to fisherman and are harvested to be used as bait. We find that nearly 100 percent of these crabs could go on to reproduce.
The second stage is the soft shell stage, which is when the crab has grown old enough (and large enough) that it goes through it's molting process. We find that nearly 100 percent of these crabs would reproduce if they were not harvested. The third stage of a female crab is the mature stage, when the female crab no longer molts and thus becomes invaluable as the "softshell crab" commodity."
Mr. Giove has complained to the Maryland Department of Natural Resources.
He says that the MDNR has told him "that the crabs are just going through a cycle and they will be plentiful in the future." His and our complaints of over harvesting of the female crab population is one very strong reason why there is a decline of the blue crab population in the Chesapeake Bay and bays along and near Ocean City, Maryland. Along with sea grass destruction by clam boats and the protective areas for the soft shell crab's molting process.
The MDNR has told Mr. Giove that as long as there is at least 10 percent of the female crab stock remaining, there will be enough females to maintain the crab
population at a sustainable level.
Mr. Giove has compiled some figures from the DNR and questions some of the regulations recently adopted for Maryland waters and the harvesting of the
blue crab by fisherman.
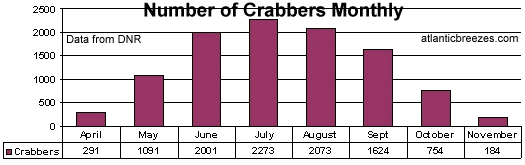
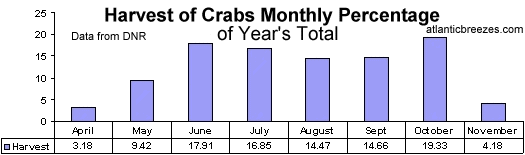
When looking at these figures the question arises why there is so much emphasis being placed on closing down the blue crab harvesting late in
the season when:
1.) There are significantly fewer crabbers.
2.) The harvest of the blue crab is nearly the lowest.
The presentation of these figures is to show that too much attention is being place on the aggregate harvesting of blue crabs. Whereas the emphasis of the decline in the blue crab should be placed, if at least, include the harvesting, and thus restrictions on the harvesting of the female blue crab.
Although the chosen "blue crab" for its flavor is the male blue crab, female hard shell crabs are increasingly harvested and sold. Originally female hard crabs were only at a discount because the female crab lacks the "flavor" of the male crab. But, as the price of the male hard crab has sky rocketed in the last few years, more and more female crabs are harvested and sold in substitution for the male crab's reduction in supply.
Ten years and fifteen ago it was very rare to find female hard shell crabs harvested and sold.
As the demand for the blue crab continues to increase, the substitution of the female crab will be made in the harvest, the production of packaged crabmeat, and the sales, further reducing the female crab population.
As the demand overseas and at home for the softshell crab (molting female crab) increases, the female crab population will further decrease.
Thus reduction in the blue crab population should be addressed by the restrictions on the harvesting of the female crab.
If China wanted to curb it's over population problems, they would pursue
the policies on the female blue crab.
For the Chesapeake Bay, Coastal Bays of Ocean City Maryland and Virginia, the repopulating of animal species and restoration of water quality must be a combined effort and not done on a state by state basis.
Author: Robert V. Lotier
Webmaster: atlanticbreeze.com
Ocean City Maryland's Internet Magazine.
Bibliography for data:
Maryland Department of Natural Resources.
Virginia Department of Natural Resources.
Maryland Sea Grant College MD .
Personal information of crabs obtained by Korean wholesale
markets by Robert V. Lotier
Graphs orginally created atlanticbreezes.com .
|




![]() Weather
Weather![]() Useful
Town Information
Useful
Town Information ![]() Watersports
Ocean Sports
Watersports
Ocean Sports![]()
![]() Dining
Crabs Restaurants
Dining
Crabs Restaurants ![]() Articles
and News
Articles
and News![]() Skateboarding
and Bicycles
Skateboarding
and Bicycles![]()
![]() Golf
Courses Town Parks Camping Vacilities
Golf
Courses Town Parks Camping Vacilities ![]()
![]() Town
Events and Holiday Activities
Town
Events and Holiday Activities ![]() Editorials
Editorials ![]()
